In the digital age, online software has become the backbone of modern businesses, educational institutions, and individuals alike. From productivity tools to collaboration platforms, e-software solutions have revolutionized the way we work, learn, and connect. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of e-software, exploring its evolution, functionalities, benefits, and future prospects.
Evolution of Online Software:
The evolution of online software can be traced back to the early days of the internet, with the emergence of web-based applications such as email clients and early collaboration tools. However, it was not until the advent of cloud computing that e-software truly began to flourish.
Cloud computing revolutionized the way software was delivered and accessed, enabling users to access applications and data over the internet, without the need for physical installation or local storage. This shift paved the way for the proliferation of Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions, which offered subscription-based access to online software applications hosted on remote servers.
Key Features and Functionalities of Online Software:
- Accessibility: Online software offers anytime, anywhere access to applications and data, enabling users to work, collaborate, and communicate from any device with an internet connection. This flexibility enhances productivity, facilitates remote work, and accommodates diverse workstyles and preferences.
- Collaboration: Online software facilitates real-time collaboration and communication among distributed teams, enabling users to share documents, collaborate on projects, and communicate via chat, video conferencing, and virtual whiteboards. Collaboration features enhance teamwork, streamline communication, and foster innovation and creativity.
- Scalability: Online software solutions are scalable, allowing organizations to easily scale their software usage and storage capacity to accommodate changing business needs and growth. Cloud-based infrastructure enables automatic scaling of resources, ensuring optimal performance and reliability even during peak usage periods.
- Security: Online software providers implement robust security measures to protect users’ data and privacy, including encryption, authentication, and access controls. Cloud-based solutions offer secure data storage and backup, minimizing the risk of data loss or breaches and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Integration: Online software solutions often offer integration capabilities with other applications and services, enabling seamless data exchange and workflow automation. Integration with third-party tools, such as project management software, CRM systems, and accounting platforms, enhances productivity and streamlines business processes.
Benefits of Online Software:
- Cost-effectiveness: Online software solutions typically follow a subscription-based pricing model, eliminating the need for upfront hardware and software investments. This cost-effective pricing structure enables businesses to access advanced software functionalities without the need for significant capital expenditure.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Online software solutions offer flexibility and scalability, allowing organizations to scale their software usage and storage capacity according to their changing needs and requirements. This flexibility enables businesses to adapt to market dynamics, seasonal fluctuations, and growth opportunities.
- Accessibility and Mobility: Online software solutions offer anytime, anywhere access to applications and data, enabling users to work, collaborate, and communicate from any location and device with an internet connection. This accessibility enhances mobility, facilitates remote work, and accommodates diverse workstyles and preferences.
- Collaboration and Communication: Online software solutions facilitate real-time collaboration and communication among distributed teams, enabling users to share documents, collaborate on projects, and communicate via chat, video conferencing, and virtual whiteboards. Collaboration features enhance teamwork, streamline communication, and foster innovation and creativity.
- Security and Compliance: Online software providers implement robust security measures to protect users’ data and privacy, including encryption, authentication, and access controls. Cloud-based solutions offer secure data storage and backup, minimizing the risk of data loss or breaches and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
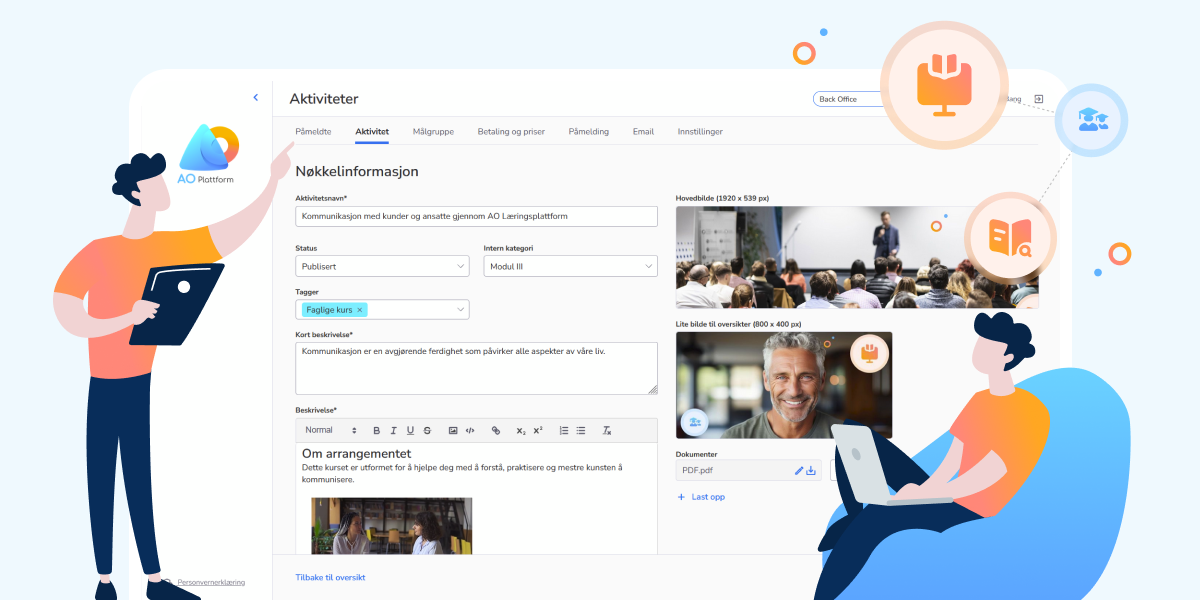
Popular Categories of Online Software:
- Productivity Tools: Productivity tools include word processors, spreadsheets, presentation software, and note-taking applications that enable users to create, edit, and share documents, presentations, and notes collaboratively.
- Project Management Software: Project management software enables teams to plan, track, and manage projects, tasks, and deadlines, facilitating collaboration, communication, and resource allocation.
- Collaboration Platforms: Collaboration platforms include messaging apps, video conferencing software, and virtual whiteboards that enable real-time communication and collaboration among distributed teams.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM systems enable businesses to manage customer interactions, track leads and sales opportunities, and analyze customer data to improve marketing, sales, and customer service efforts.
- Accounting and Financial Management Software: Accounting and financial management software enables businesses to manage financial transactions, track expenses and revenue, generate invoices, and streamline accounting processes.
Future Trends in Online Software:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies will enhance the capabilities of e-software solutions, enabling predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and personalized user experiences.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing will enable e-software solutions to process data and perform computations closer to the source, reducing latency, improving performance, and enhancing security and privacy.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology will enable secure and transparent transactions and data exchanges within e-software solutions, enhancing trust, integrity, and auditability.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Integration with IoT devices will enable e-software solutions to collect, analyze, and act on real-time data from connected devices, enabling smarter decision-making and automation.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Integration with AR and VR technologies will enable e-software solutions to deliver immersive and interactive user experiences, enhancing training, education, and entertainment applications.
Conclusion:
Online software has become an integral part of modern life, empowering businesses, educational institutions, and individuals to work, collaborate, and communicate more effectively and efficiently. With their flexibility, scalability, accessibility, and security, e-software solutions enable organizations to adapt to changing business environments, enhance productivity, and drive innovation.
As technology continues to evolve and new trends emerge, the future of e-software holds immense potential for transforming the way we work, learn, and connect. By embracing the latest advancements and innovations in online software, organizations and individuals can unlock new opportunities, solve complex challenges, and shape a more connected, intelligent, and collaborative future.
